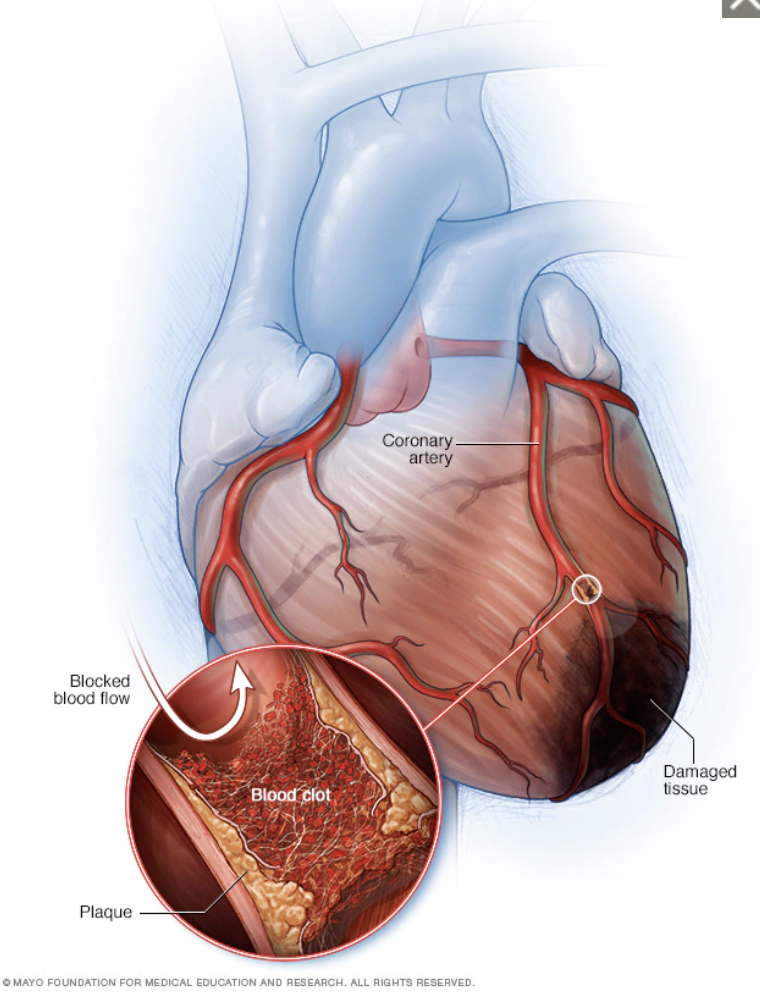
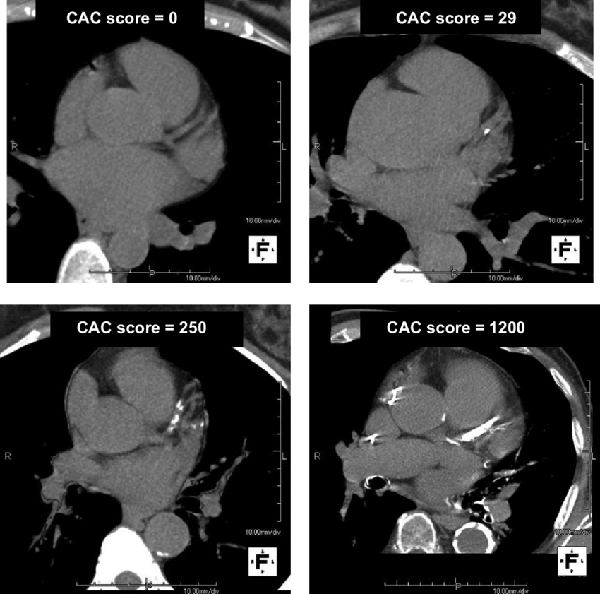
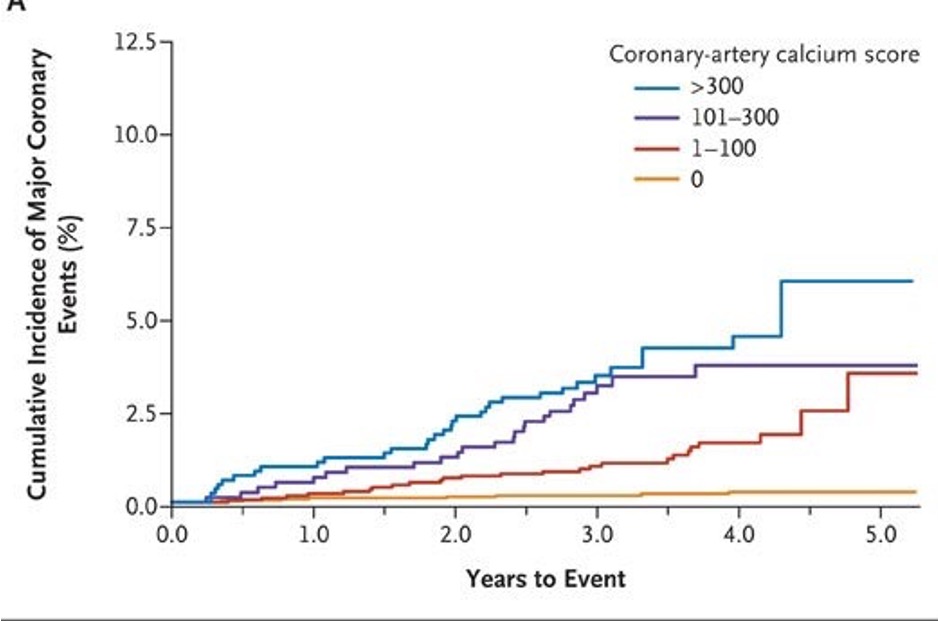
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) score has emerged as an accurate and simple method to screen for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease risk. The amount of calcium in the arteries correlates with overall plaque burden and greatly enhances the ability to predict risk of heart attack and cardiovascular death.
Case Studies:
Two male patients with family history of coronary disease. Neither has angina with exercise. Both would have low calculated risk by the usual ACC risk calculator. Although the younger patients has additional risk factors for CVD (fatty liver, cigar smoking), he is fortunate to have no CAC.